When designing or maintaining linear motion systems, selecting the appropriate components is crucial for achieving optimal performance and efficiency. Among the various options available, linear guides and linear bearings are two of the most commonly used. While both facilitate linear motion, they have distinct characteristics that make them suitable for different applications. This article explores the differences between linear guides and linear bearings, helping you make an informed decision based on your specific needs.
Linear Bearings: Simplicity and Versatility
Linear bearings are essential components in linear motion systems designed to provide smooth and low-friction motion along a linear axis. They typically consist of an outer cylinder (the outer race) and an inner cylinder (the inner race). The inner race is mounted on a shaft, while the outer race is installed inside a housing or frame.
Advantages of Linear Bearings:
- Simplicity: Linear bearings are relatively straightforward in design and installation, making them easy to integrate into various systems.
- Versatility: They can be used across a wide range of applications and are available in different types, such as ball bearings and roller bearings. Ball bearings are ideal for high-speed applications due to their low friction, while roller bearings are better suited for handling heavy loads and providing increased rigidity.
- Cost-Effective: Linear bearings are generally more affordable, making them an attractive option for applications with moderate requirements and budget constraints.
Considerations for Linear Bearings:
- Load Capacity: They are suitable for moderate loads but may not be ideal for very heavy applications.
- Precision: While they offer smooth motion, they may not provide the same level of precision and rigidity as linear guides.
Linear Guides: Precision and Stability
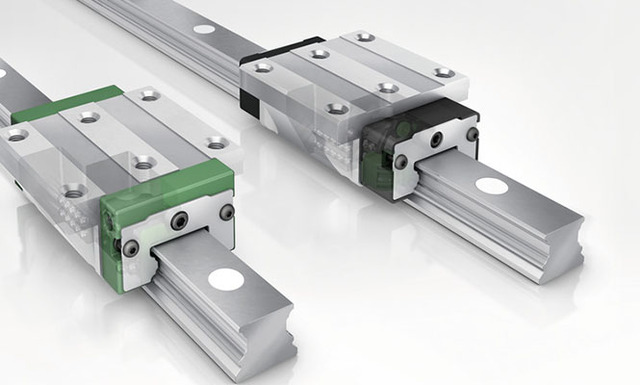
Linear guides are designed to deliver high precision and stability. They consist of a linear rail and a carriage that moves along the rail. The rail is mounted to a frame or structure, while the carriage supports the load and enables smooth linear motion.
Advantages of Linear Guides:
- Precision and Rigidity: Linear guides are engineered for high accuracy and repeatability. They are commonly used in applications requiring precise positioning, such as CNC machines and semiconductor manufacturing equipment.
- High Load Capacity: They can handle heavier loads compared to linear bearings, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Durability: Linear guides often have an enclosed design, which provides better resistance to contaminants, dust, and debris.
Considerations for Linear Guides:
- Cost: Linear guides are generally more expensive than linear bearings, which might impact budget considerations.
- Complexity: They may require more elaborate installation and maintenance procedures compared to simpler linear bearings.
Factors to Consider When Choosing
When deciding between linear guides and linear bearings, consider the following factors:
- Load Capacity: Evaluate the weight and type of load your system needs to support. Linear guides are typically better suited for handling heavier loads.
- Precision Requirements: For applications demanding high precision and repeatability, linear guides are usually the superior choice.
- Speed and Acceleration: Ball bearings within linear bearings are ideal for high-speed and rapid acceleration applications due to their low friction properties.
- Environment: Consider environmental factors such as exposure to contaminants. Linear guides often offer better protection due to their enclosed design.
- Budget: Linear bearings are generally more cost-effective and may be preferable for applications with moderate requirements.
- Maintenance: Linear bearings often require less maintenance due to having fewer moving parts.
Choosing the Right Option
Choose Linear Bearings when:
- Your budget is limited, and high precision or rigidity is not critical.
- The application involves moderate loads and speeds.
- You need a versatile solution that is easy to install and replace.
Choose Linear Guides when:
- Your application demands high precision, repeatability, and rigidity.
- You need to handle heavy loads.
- Environmental conditions require greater protection from contaminants.
By carefully evaluating these factors and consulting with experts or suppliers, you can select the most suitable component for your linear motion system, ensuring optimal performance and efficienc