Choosing a linear guide involves several considerations to ensure it meets the specific needs of your application. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you make an informed decision:
1. Define Your Application Requirements
- Load Capacity: Determine the maximum load the linear guide needs to support, including static and dynamic loads.
- Speed and Acceleration: Consider the speeds and acceleration rates the guide will need to handle.
- Accuracy and Precision: Identify the level of precision required for your application.
- Operating Environment: Evaluate environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, dust, and exposure to chemicals.
2. Choose the Type of Linear Guide
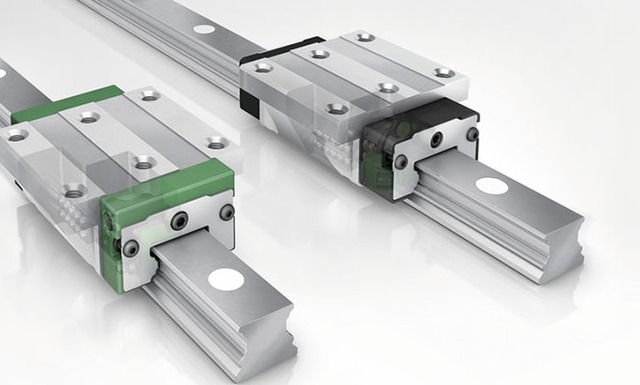
- Rail and Block (Linear Guides): Suitable for high-load applications and provides high precision.
- Round Shaft Bearings: Often used in lower-load applications and where cost is a concern.
- Profile Rail Guides: Offer high rigidity and are ideal for high-load and high-precision applications.
3. Consider Load Distribution
- Point Contact vs. Line Contact: Line contact (like with profile rail guides) is better for distributing loads evenly and can handle higher loads and moments compared to point contact.
4. Evaluate the Material and Construction
- Materials: Common materials include steel, aluminum, and stainless steel. Choose based on strength requirements and environmental conditions.
- Construction: Consider factors such as corrosion resistance, lubrication, and ease of maintenance.
5. Check for Compatibility with Existing Systems
- Ensure the linear guide is compatible with your existing system or machinery in terms of mounting and integration.
6. Assess the Cost and Value
- Balance between cost and performance. Sometimes a higher initial cost may lead to better performance and lower maintenance costs in the long run.
7. Review Manufacturer Specifications and Support
- Look at technical datasheets and manufacturer recommendations.
- Consider the availability of technical support and after-sales service.
8. Prototype and Testing
- If possible, test the linear guide in a prototype setup to ensure it meets all performance criteria before full-scale implementation.
Summary
Selecting the right linear guide involves understanding your application’s load, speed, precision, and environmental needs. By considering these factors, choosing the appropriate type, material, and ensuring compatibility, you can select a linear guide that optimally meets your requirements.